Georg Brandes
| Georg Brandes | |
|---|---|
 Georg Brandes, a sketch for a painting, by P.S. Krøyer, 1900 |
|
| Born | Georg Morris Cohen Brandes 4 February 1842 Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Died | 19 February 1927 (aged 85) |
| Occupation | Critic |
| Nationality | Danish |
| Education | University of Copenhagen |
| Relative(s) | Edvard Brandes (brother) |
|
|
|
| Signature | 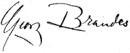 |
Georg Morris Cohen Brandes (4 February 1842 – 19 February 1927) was a Danish critic and scholar who had great influence on Scandinavian and European literature from the 1870s through the turn of the 20th century. He is seen as the theorist behind the "Modern Breakthrough" of Scandinavian culture. At the age of 30, Brandes formulated the principles of a new realism and naturalism, condemning hyper-aesthetic writing and fantasy in literature. According to Brandes, literature should be an organ "of the great thoughts of liberty and the progress of humanity." His literary goals were shared by many authors, among them the Norwegian realist playwright Henrik Ibsen.
When Georg Brandes held a series of lectures in 1871 with the title "Main Currents in 19th-century Literature," he defined the Modern Breakthrough and started the movement that would become Cultural Radicalism. In 1884 Viggo Hørup, Georg Brandes, and his brother Edvard Brandes started the daily newspaper Politiken with the motto: "The paper of greater enlightenment." The paper and their political debates led to a split of the liberal party Venstre in 1905 and created the new party Det Radikale Venstre.
Contents |
Biography
Youth
Georg Brandes was born in Copenhagen in a non-orthodox Jewish middle-class family, the elder brother of prominent Danes Ernst Brandes and Edvard Brandes. He became a student at the University of Copenhagen in 1859 where he first studied jurisprudence. From this, however, his interests soon turned to philosophy and aesthetics. In 1862 he won the gold medal of the university for an essay on The Idea of Nemesis among the Ancients. Before this, indeed since 1858, he had shown a remarkable gift for verse-writing, the results of which, however, were not abundant enough to justify separate publication. Brandes did not collect his poems until as late as 1898. At the university, which he left in 1864, Brandes was influenced by the writings of Heiberg in criticism and Søren Kierkegaard in philosophy, influences which continued to leave traces on his work.[1]

In 1866, he took part in the controversy raised by the works of Rasmus Nielsen in a treatise on "Dualism in our Recent Philosophy." From 1865 to 1871 he traveled much in Europe, acquainting himself with the condition of literature in the principal centers of learning. His first important contribution to letters was his Aesthetic Studies (1868), where his maturer method is already foreshadowed in several brief monographs on Danish poets. In 1870 he published several important volumes, The French Aesthetics of the Present Day, dealing chiefly with Hippolyte Taine, Criticisms and Portraits, and a translation of The Subjection of Women by John Stuart Mill, whom he had met that year during a visit to England.[1]
The Modern Breakthrough
Brandes now took his place as the leading northern European critic, applying to local conditions and habits of thought the methods of Taine. He became docent or reader in Belles Lettres at the University of Copenhagen,[1] where his lectures were a great success and gathered huge audiences.[2] His famous opening lecture on 3 November 1871, Hovedstrømninger i det 19de Aarhundredes Litteratur (English: Main Currents in the Literature of the Nineteenth Century), signalled the beginning of his life-long struggle to modernize Danish literature.[3] On the professorship of Aesthetics becoming vacant in 1872, it was taken as a matter of course that Brandes would be appointed. But the young critic had offended many sensibilities by his ardent advocacy of modern ideas; he was known to be a Jew, his convictions were Radical, he was suspected of being an atheist. The authorities refused to elect him, but his fitness for the post was so obvious that the chair of Aesthetics remained vacant, no one else daring to place himself in comparison with Brandes.[1]

In the midst of these polemics, Brandes began to issue the most ambitious of his works, Main Currents in the Literature of the Nineteenth Century, of which four volumes appeared between 1872 and 1875 (English translation, 1901–1905). The brilliant novelty of this criticism of the literature of major European countries at the beginning of the 19th century, and his description of the general revolt against the pseudo-classicism of the 18th century, at once attracted attention outside Denmark. The tumult which gathered round the person of the critic increased the success of the work, and the reputation of Brandes grew apace, especially in Germany and Russia.[1]
In 1877 Brandes left Copenhagen and settled in Berlin, taking a considerable part in the aesthetic life of that city. His political views, however, made Prussia uncomfortable for him, and he returned in 1883 to Copenhagen, where he found a whole new school of writers and thinkers eager to receive him as their leader.[1] He headed the group "Det moderne Gjennembruds Mænd" (The Men of the Modern Breakthrough), comprising of J.P. Jacobsen, Holger Drachmann, Edvard Brandes, Erik Skram, Sophus Schandorph, and Norwegians Henrik Ibsen and Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson,[3] but a conservative reaction against his "realistic" doctrines began around 1883, headed by Holger Drachmann.[3]
Later authorship
Among his later writings must be mentioned the monographs on Søren Kierkegaard (1877), on Esaias Tegnér (1878), on Benjamin Disraeli (1878), Ferdinand Lassalle (in German, 1877), Ludvig Holberg (1884), on Henrik Ibsen (1899) and on Anatole France (1905). Brandes wrote with great depth on the main contemporary poets and novelists of Denmark and Norway, and he and his disciples were for a long time the arbiters of literary fame in the north. His Danish Poets (1877), containing studies of Carsten Hauch, Ludvig Bødtcher, Christian Winther, and Paludan-Müller, his Men of the Modern Transition (1883), and his Essays (1889), are volumes essential to the proper study of modern Scandinavian literature. He wrote an excellent book on Poland (1888; English translation, 1903), and was one of the editors of the German version of Ibsen.[1]
The most important of his later works was his study of William Shakespeare (1897–1898), which was translated into English by William Archer, and was highly acclaimed. It was, perhaps, the most authoritative work on Shakespeare, not principally intended for an English-speaking audience, which had been published in any country.[1] He was afterwards engaged on a history of modern Scandinavian literature. In his critical work, which extended over a wider field than that of any other living writer, Brandes was aided by a singularly charming style, lucid and reasonable, enthusiastic without extravagance, brilliant and colored without affectation. In 1900 he collected his works for the first time in a complete and popular edition, and began to work on a German edition, completed in 1902.[1]
Personal life and last years
In the late 1880s, Brandes fought against what he saw as the hypocrisy of prudish sexuality, which caused a rift with Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson.[4] Between the years of 1886 and 1888 Brandes was engaged in a relationship with the Swedish authoress Victoria Benedictsson, who wrote "Penningar" and "Fru Marianne" under the male pseudonym Ernst Ahlgren. Victoria Benedictsson committed suicide in a Copenhagen hotel room,[5] and the relationship with Brandes has later been blamed as the cause for the death.[4]
In 1890, Brandes turned to concentrating on "great personalities" as the source of culture. In this period, he discovered Friedrich Nietzsche whom he introduced to Scandinavian culture. Brandes, in an 1888 letter, wrote to Nietzsche advising him to read the works of Kierkegaard. He described Nietzsche's philosophy as "aristocratic radicalism", a description which delighted Nietzsche, and the idea of "aristocratic radicalism" influenced most of the later works of Brandes and resulted in voluminous biographies Wolfgang Goethe (1914–15), Francois de Voltaire (1916–17), Gaius Julius Cæsar 1918 and Michelangelo (1921).[3]
In the 1900s, he fought the Danish political establishment on several occasions, but eventually had to curb his acidic attacks. However, his international reputation was growing.[4] In many ways he emulated his own assessment of Voltaire, as an author against habitual thinking, hypocrisy and the thin veneer of morality.[3] He condemned the maltreatment of national minorities, the persecution of Dreyfus etc. During World War I he condemned the national aggression and imperialism on both sides and his last years were dedicated to anti-religious polemic. In this late period he made new connections to intellectuals like Henri Barbusse and Romain Rolland when he was co-signer in the foundation of Clarté, as well as E. D. Morel.[4]
Legacy
Brandes stands as one of the most influential inspirations of Danish culture, an equal of Holberg, Grundtvig, and Ansgar. Among his supporters, Brandes' work was seen as a liberator from repressive norms, authority and hypocrisy, and he served as an inspiration for many contemporary writers. On the other hand, conservative circles condemned him as an immoral, unpatriotic and subversive blasphemer; as he became the lynchpin of criticism against modernity in its entirety.[4] At the same time, some socialists criticized his elitist attitudes, while some feminists have regarded his attitude of sexual equality as being inconsequential.[4]
His brother Edvard Brandes (1847–1931), also a well-known critic, was the author of a number of plays, and of two psychological novels: A Politician (1889), and Young Blood (1899). He became an outstanding political figure of the party Det Radikale Venstre.[3]
Quotations
- Being gifted requires courage (1869)
- That a literature in our time is living is shown in that way that it debates problems. (1871)[needs correction?]
- Poor is the power of the lead that becomes bullets compared to the power of the hot metal that becomes types. (1900)
- He who does not understand a joke, he does not understand Danish (1906)
- The Danish glee: the national version of cheerfulness. (1909)
- The stream of time sweeps away errors, and leaves the truth for the inheritance of humanity
- It would be as impossible for me to attack Christianity as it would be impossible for me to attack werewolves.[6]
See also
- Helen Zelezny-Scholz
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Encyclopedia Britannica, 1911, "Georg Morris Cohen Brandes"
- ↑ Ole Friis Thellufsen, Artikel: Georg Brandes, Aarhus University, July 29, 2009
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Georg Brandes at Gyldendals Åbne Encyklopædi
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Georg Brandes – Forfatterportræt ved Jørgen Knudsen at Arkiv for Dansk Litteratur
- ↑ Victoria Benedictsson at Gyldendals Åbne Encyklopædi
- ↑ From the Selected Letter of Friedrich Nietzsche, Brandes to Nietzsche, 23rd November 1888
Further reading
- Bertil Nolin: Georg Brandes. Gloucester, Mass., 1976.
- Hans Hertel (ed.): The Activist Critic. A Symposium on the Political Ideas, Literary Methods and International Reception of Georg Brandes. Copenhagen, 1980.
- Doris R. Asmundsson: Georg Brandes. Aristocratic Radical. N. Y., 1981.
- W. Glyn Jones (ed.): Georg Brandes. Selected Letters. Norvik Press, 1990.